VR, AR, and XR Explained: The Future is Here
Dive into this comprehensive guide to understand the differences, similarities, and real-world applications of VR, AR, and XR.
Immersive. Interactive. Practical. Transformative.
Imagine you’re shopping online for a new couch. Instead of guessing whether it will fit in your living room, you pull out your phone, open an app, and see a 3D version of the couch projected into your actual space. Platforms like Amazon and other retailers are already offering this experience through Augmented Reality (AR), making it easier than ever to visualize products in your home.

This is not the future; it’s happening now. Consider Meta’s latest advancements in Virtual Reality (VR), where people host virtual concerts, attend work meetings in 3D offices, and even learn surgery in fully immersive digital environments.
With Apple’s Vision Pro making waves and companies like NVIDIA pushing Extended Reality (XR) applications to new levels, it’s clear that immersive tech is here to stay. But what exactly are these technologies, and how do they differ? Let’s break it down
What Are VR, AR, and XR?
At their core, VR, AR, and XR are all about creating immersive experiences. However, they achieve this in different ways:
- Virtual Reality (VR) is a fully immersive experience that transports users into a completely digital environment. By wearing a VR headset, you’re cut off from the physical world and placed into a simulated one. Think of it as stepping into a video game or a 3D movie, where you can look around, interact, and even move within the virtual space.

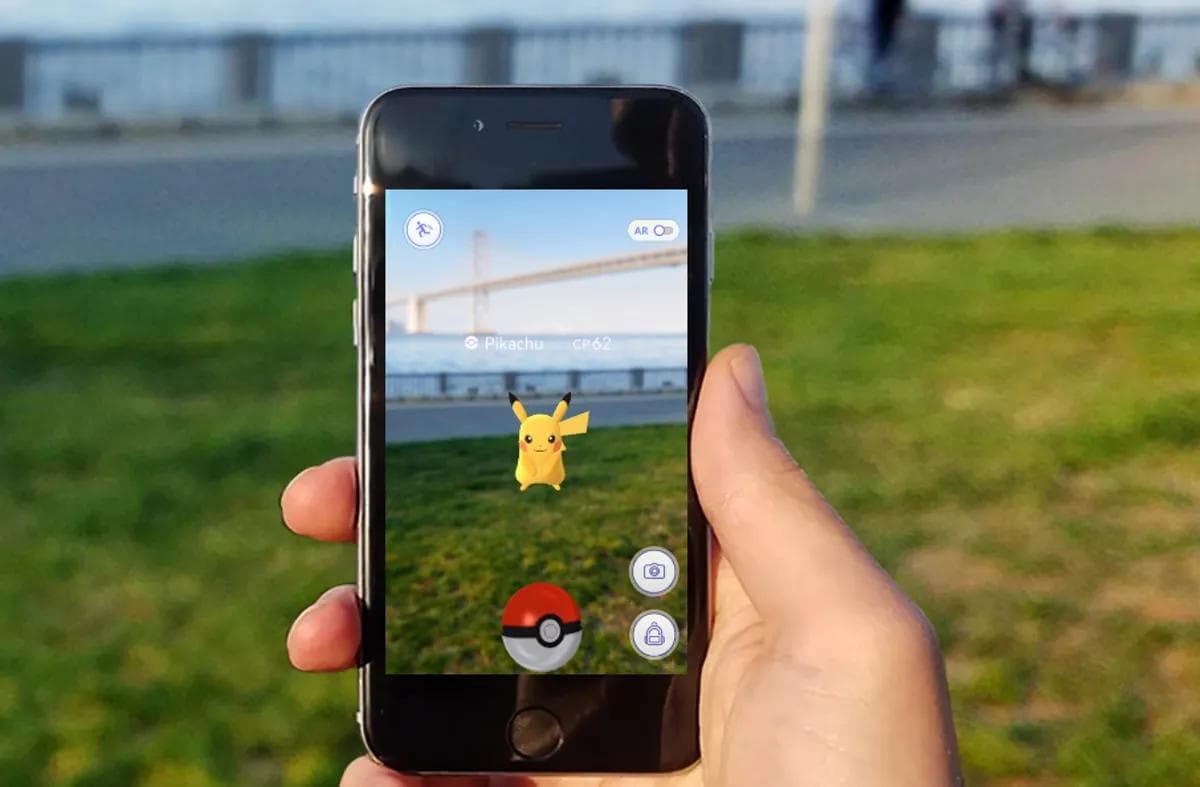
- Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital elements onto the real world. Instead of replacing your surroundings, AR enhances them. A classic example is Pokémon GO, where digital creatures appear in your real-world environment through your smartphone camera. AR is often experienced through smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses like Microsoft’s HoloLens.

- Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses VR, AR, and everything in between. It represents the spectrum of immersive technologies, from fully virtual to fully real, with mixed reality (MR) sitting somewhere in the middle. XR is about blending the physical and digital worlds seamlessly, creating experiences that can adapt to the user’s needs.
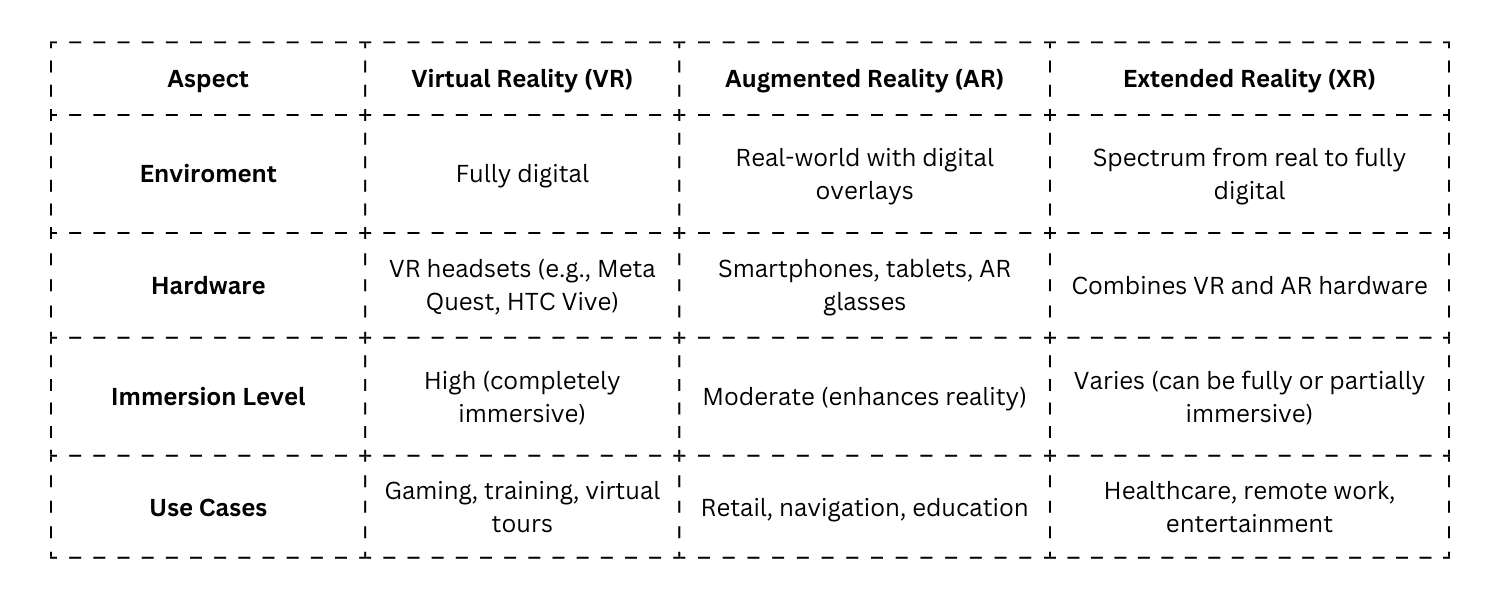
How Do They Differ?
While VR, AR, and XR share the goal of immersion, they differ in their approach and application. Here’s a breakdown:
The Technology Behind the Magic
The magic of VR, AR, and XR lies in the sophisticated technology that powers them. Here’s a closer look at what makes these experiences possible:
- Sensors and Cameras: Both VR and AR rely heavily on sensors and cameras to track movement and orientation. In VR, this allows you to look around and interact with the virtual world. In AR, it helps the device understand the real world and place digital objects accurately.
- Displays: High-resolution displays are crucial for creating realistic visuals. VR headsets use two screens (one for each eye) to create a 3D effect, while AR devices often use transparent displays to overlay digital content onto the real world.
- Processing Power: Immersive experiences require significant computational power. Whether it’s rendering a detailed virtual environment or processing real-time data for AR overlays, powerful processors and GPUs are essential.
- Software and Platforms: The software ecosystem is what brings these technologies to life. Platforms like Unity and Unreal Engine are commonly used to develop VR and AR applications, while XR frameworks enable seamless integration across devices.
Did you know the Las Vegas Sphere uses around 150 RTX A6000 graphics cards—each costing $4,500—to power its mind-blowing visuals? This $2.3 billion venue relies on this massive computational power to run 16k by 16k displays inside and 1.2 million programmable LED pucks on its exterior. It’s a true testament to the sheer processing power needed to create immersive experiences.
Similarities Between VR, AR, and XR
Despite their differences, VR, AR, and XR share several commonalities:
- Immersive Experiences: All three technologies aim to create experiences that engage users in ways traditional media cannot.
- Interactivity: Whether it’s picking up a virtual object or interacting with a digital overlay, user interaction is a key component.
- Applications Across Industries: From entertainment to healthcare, these technologies are transforming how we work, learn, and play.
Use Cases: Where Do VR, AR, and XR Shine?
The applications of VR, AR, and XR are vast and varied. Here are some real-world examples:
1. Gaming and Entertainment
- VR: Games like Beat Saber and Half-Life: Alyx offer fully immersive experiences that transport players into new worlds.
- AR: Pokémon GO and Snapchat filters are popular examples of AR in entertainment.
- XR: Mixed reality games like Minecraft Earth blend the real and virtual worlds, allowing players to build and explore in their own environment.
2. Education and Training
- VR: Medical students can practice surgeries in a risk-free virtual environment.
- AR: AR apps can bring textbooks to life, showing 3D models of the human body or historical artifacts.
- XR: XR platforms enable remote learning, where students can interact with virtual labs or attend virtual classrooms.
3. Healthcare
- VR: Used for pain management, physical therapy, and even treating PTSD.
- AR: Surgeons can use AR to overlay patient data during procedures.
- XR: Combines VR and AR for comprehensive training and diagnostic tools.
4. Retail and Marketing
- VR: Virtual showrooms allow customers to explore products in a 3D space.
- AR: Amazon's AR app feature lets users visualize how furniture will look in their homes.
- XR: Brands are using XR to create interactive marketing campaigns that blend physical and digital experiences.
5. Remote Work and Collaboration
- VR: Virtual meeting spaces like Horizon Workrooms enable teams to collaborate in a shared virtual environment.
- AR: AR glasses can provide real-time information and guidance for field workers.
- XR: XR platforms are being used for remote assistance, where experts can guide on-site workers through complex tasks.
The Future of Immersive Technologies
As VR, AR, and XR continue to evolve, their potential is limitless. We’re already seeing the beginnings of a metaverse—a collective virtual shared space that blends the physical and digital worlds. Companies like Meta (formerly Facebook) are investing heavily in this vision, aiming to create a future where we can live, work, and play in immersive environments.
However, challenges remain. Issues like motion sickness in VR, the high cost of AR glasses, and the need for more robust XR ecosystems must be addressed. But as technology advances and becomes more accessible, these barriers will likely diminish.
Final Thoughts
VR, AR, and XR are more than just buzzwords—they’re transformative technologies that are reshaping how we interact with the world. Whether it’s exploring a virtual landscape, enhancing your surroundings with digital overlays, or seamlessly blending the two, these immersive experiences are here to stay.
At BlueClod, we’re excited to be part of this journey, helping businesses and individuals harness the power of VR, AR, and XR to create meaningful and impactful experiences. The future is immersive, and it’s closer than you think.
So, what will you create in this brave new world? The possibilities are endless.
Image Credits:
- Image from CNET
- Image from About Amazon
Related Posts
Stay in the Loop with BlueClod
Sign up for updates on our latest VR advancements, cutting-edge features, and more.
